16+ Stratified Columnar Epithelium Under Microscope
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Under Microscope. In general, epithelial tissue is any group of cells lining a body cavity or body surface. Volumes in adults can range from nearly zero to 500.

Feces pass out of the rectum, through the anus, and out of the body. Attempts to insert the gene into nasal epithelium has had little success. In general, epithelial tissue is any group of cells lining a body cavity or body surface.
sto in silenzio tumblr tablier de baignoire carreler stillborn baby boy poems tableau ville de nuit
Intro to Anatomy 6 Tissues, Membranes, Organs
The large intestine feeds into the rectum, which stores the feces and has a columnar epithelium with abundant goblet cells. Stratified cuboidal epithelium describes an epithelial tissue with. 1) columnar epithelium, which lines the stomach, intestines, trachea and bronchi, salivary and other glands, pancreas, gallbladder, nasal cavity and sinuses, uterus (including inner cervix), fallopian tubes, kidneys, testes, vasa deferentia, and other ductal structures, 2) stratified squamous epithelium, which lines. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope.

In general, epithelial tissue is any group of cells lining a body cavity or body surface. In slide 29 and slide 176, this type of epithelium lines the luminal (mucosal) surface of the small and large intestines, respectively. Volumes in adults can range from nearly zero to 500. The sample is viewed under a microscope to look for blood. The.

Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. So, to correctly identify the type of tissue requires three words (e.g., simple columnar epithelium, stratified, squamous epithelium, etc. Slide 29 (small intestine) view virtual slide slide 176 40x (colon, h&e) view virtual slide remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. Refer to.

Simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells while stratified epithelium contains several layers. In general, epithelial tissue is any group of cells lining a body cavity or body surface. With our money back guarantee, our customers have the right to request and get a refund at any stage of their order in case something goes wrong. Slide.
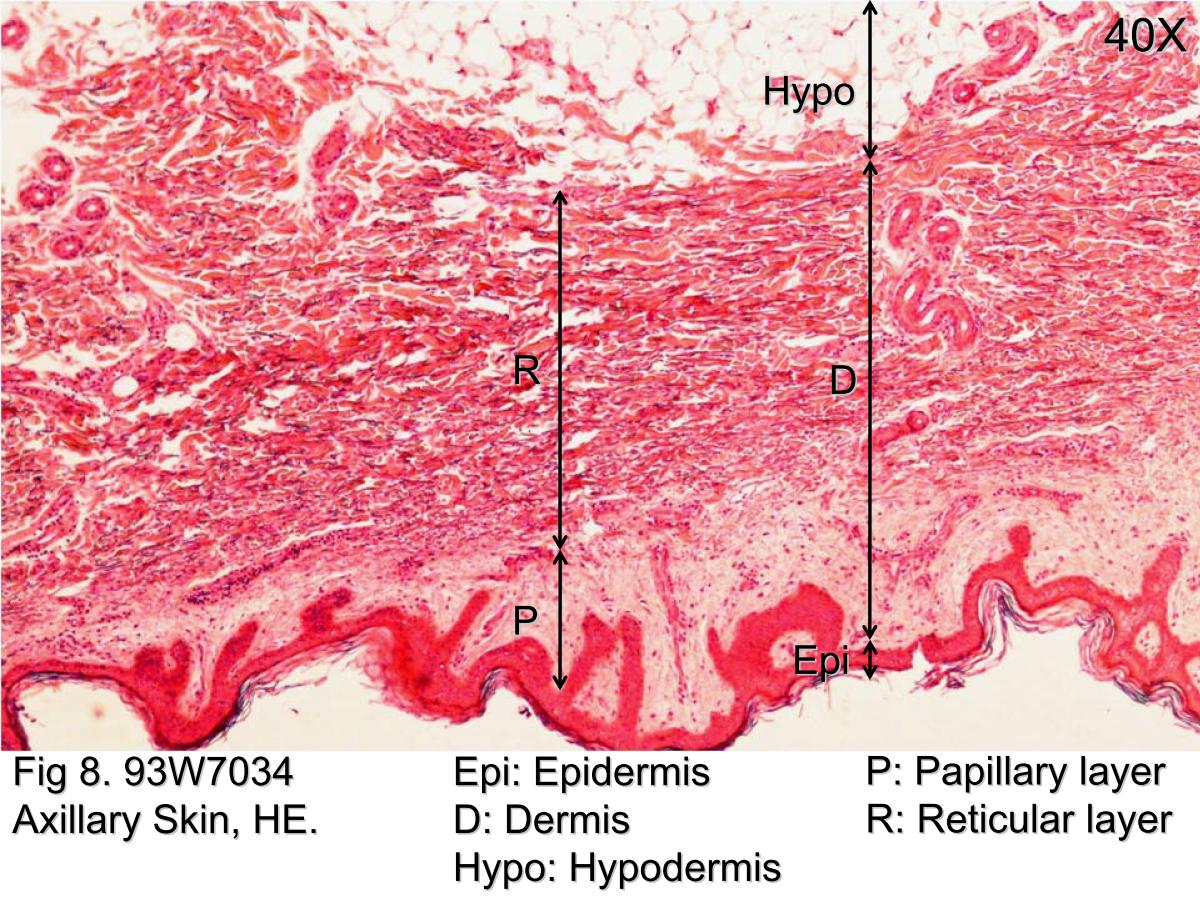
Slide 29 (small intestine) view virtual slide slide 176 40x (colon, h&e) view virtual slide remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. The cause is a gene on chromosome 7; When empty, it resembles columnar epithelia, but when stretched, it “transitions” (hence the name) to a squamous appearance (see figure 25.8.3). Stratified cuboidal epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue.

Slide 29 (small intestine) view virtual slide slide 176 40x (colon, h&e) view virtual slide remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. In histological slides stained with h/e, the bowman’s membrane is a solid pink layer directly under the epithelium. A form of cancer, carcinoma makes up the majority of the cases of malignancy. Feces pass out of the rectum,.

The sample is viewed under a microscope to look for blood. Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. In histological slides stained with h/e, the bowman’s membrane is a solid pink layer directly under the epithelium. Simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells.

The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that form the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract.composed of simple columnar epithelial cells, it serves two main functions: Refer to the diagram at the end of this chapter for the tissue orientation and. The sample is viewed under a microscope to look.