46+ Stratified Sampling Method
Stratified Sampling Method. The sampling fraction is the main differentiating factor between proportional and disproportionate stratified sampling. Other probability sampling techniques like cluster sampling and stratified random sampling can be very.
Systematic sampling is probably the easiest one to use, and Purposive sampling is used in cases where the specialty of an authority can select a more representative sample that can bring more accurate results than by using other probability sampling techniques. Each element of the population.
stillborn tattoo stickers para whatsapp memes png soudure etain argent table salle a manger ronde blanche
Sampling techniquesmod5
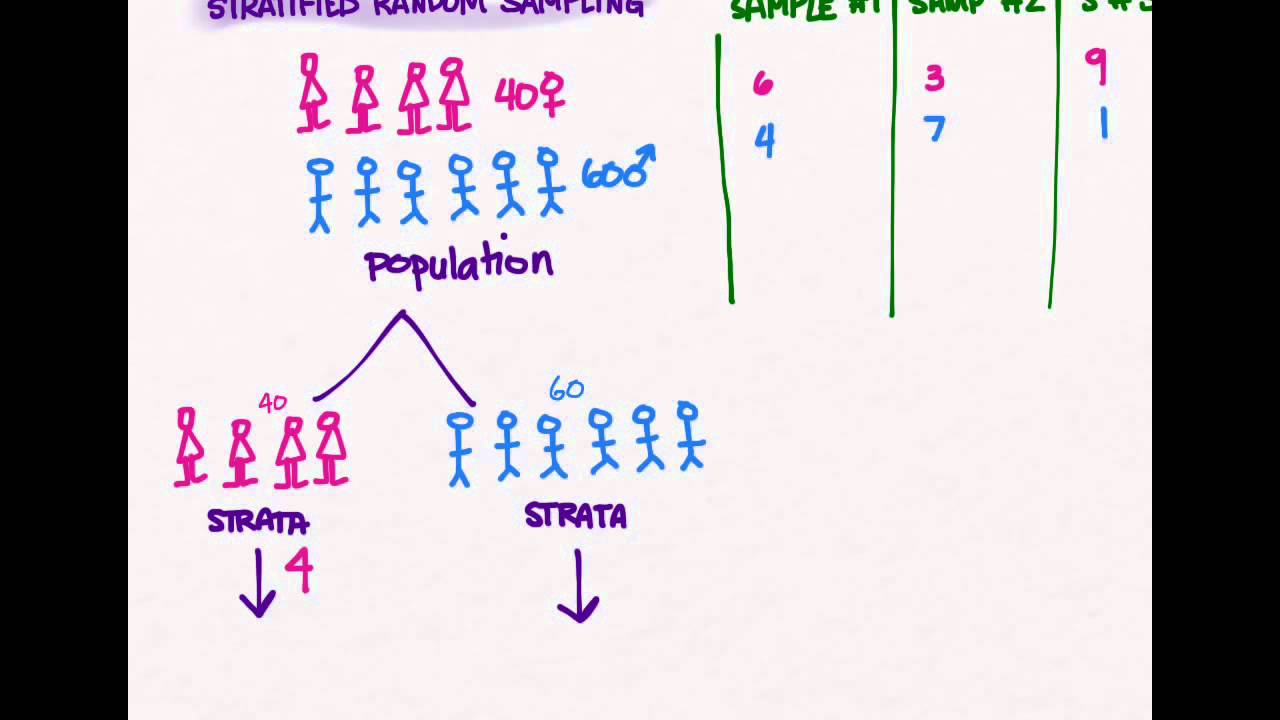
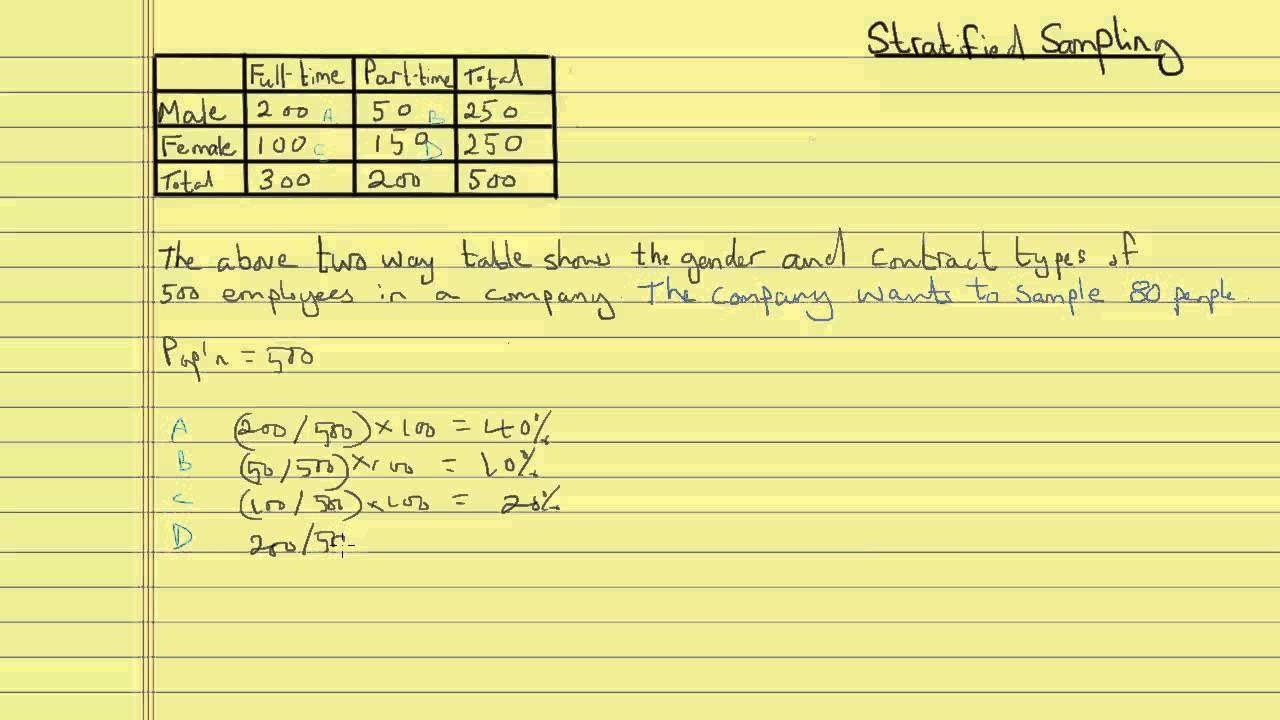
In disproportionate stratified random sampling, the different strata do not have the same sampling fractions as each other. How the variance is computed depends on the method by which the sample was taken. We did the computation just to show that if hypothetically, the data was collected by s.r.s. To use this sampling method, you divide the population into subgroups (called strata) based on the relevant characteristic (e.g.

Other probability sampling techniques like cluster sampling and stratified random sampling can be very. For example, suppose a high school principal wants to conduct a survey to collect the opinions of. To use this sampling method, you divide the population into subgroups (called strata) based on the relevant characteristic (e.g. The population is divided into h groups, called strata.; Since.

This type of sampling technique is also known as purposive sampling and authoritative sampling. The success of this sampling method depends on the precision of the investigator in assigning fractions. Each element of the population. How the variance is computed depends on the method by which the sample was taken. The sampling fraction is the main differentiating factor between proportional.
Each element of the population. Revised on october 5, 2021. You can divide your population into characteristics of importance for the research. Systematic sampling is defined as a probability sampling method where the researcher chooses elements from a target population by selecting a random starting point and selects sample members after a fixed ‘sampling interval.’. For example, suppose a high.

For example, suppose a high school principal wants to conduct a survey to collect the opinions of. Published on september 18, 2020 by lauren thomas. Purposive sampling is used in cases where the specialty of an authority can select a more representative sample that can bring more accurate results than by using other probability sampling techniques. Revised on october 5,.

For instance, if your four strata contain 200, 400, 600, and 800 people, you may choose to have different sampling fractions for each stratum. Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. We did the computation just to show that if hypothetically, the data was collected by.

Systematic sampling is defined as a probability sampling method where the researcher chooses elements from a target population by selecting a random starting point and selects sample members after a fixed ‘sampling interval.’. Systematic sampling is probably the easiest one to use, and Published on september 18, 2020 by lauren thomas. Stratified random sampling refers to a sampling method that.

Each element of the population. In disproportionate stratified random sampling, the different strata do not have the same sampling fractions as each other. Gender, age range, income bracket, job role). Stratified sampling it allows you draw more precise conclusions by ensuring that every subgroup is properly represented in the sample. Other probability sampling techniques like cluster sampling and stratified random.