38++ Stratified Sampling Definition Statistics
Stratified Sampling Definition Statistics. Suppose the fire department mandates that all fire fighters must weigh between 150 and 250 pounds. Revised on october 2, 2020.

Some examples will clarify the difference between discrete and continuous variables. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Otherwise, it is called a discrete variable.
soudeur mig mag salaire tapis sol bebe mousse interdit store voilage tabouret bas vintage
Sampling 03 Stratified Random Sampling YouTube
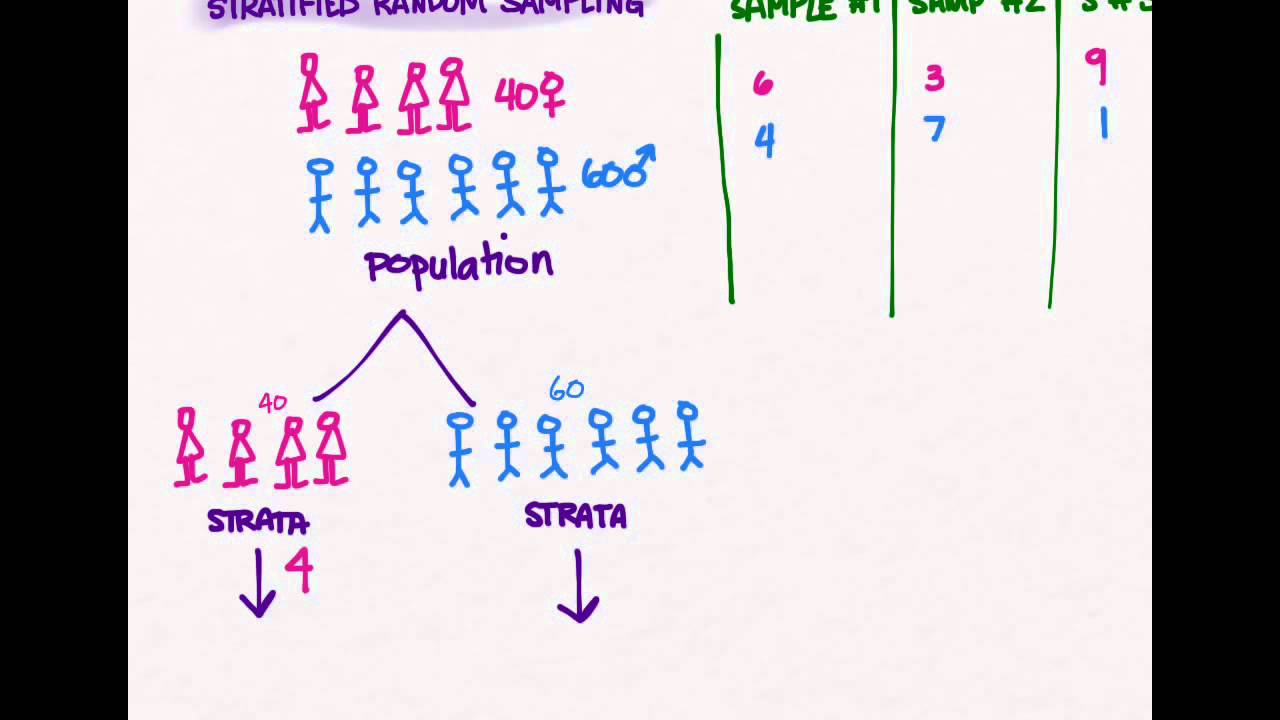
Published on august 28, 2020 by lauren thomas. Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. Otherwise, it is called a discrete variable. Revised on october 2, 2020.

Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. Revised on october 2, 2020. Published on august 28, 2020 by lauren thomas. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Otherwise, it is called.

Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata. Stratified random sampling provides the benefit of a more accurate sampling of a population, but can be disadvantageous when researchers can't classify every member of the population into a subgroup. Suppose the fire department mandates that all fire fighters.

If a variable can take on any value between its minimum value and its maximum value, it is called a continuous variable; Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Simple random sampling | definition, steps & examples. A simple random sample is a randomly selected.

Stratified random sampling provides the benefit of a more accurate sampling of a population, but can be disadvantageous when researchers can't classify every member of the population into a subgroup. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Suppose the fire department mandates that all fire.
For example, lucas can give a survey to every. Some examples will clarify the difference between discrete and continuous variables. Otherwise, it is called a discrete variable. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Simple random sampling | definition, steps & examples.