36++ Stratified Random Sampling In Research
Stratified Random Sampling In Research. Results from probability theory and statistical theory are employed to guide the practice. Each technique makes sure that each person or item considered for the research has an equal opportunity to be chosen as part of.
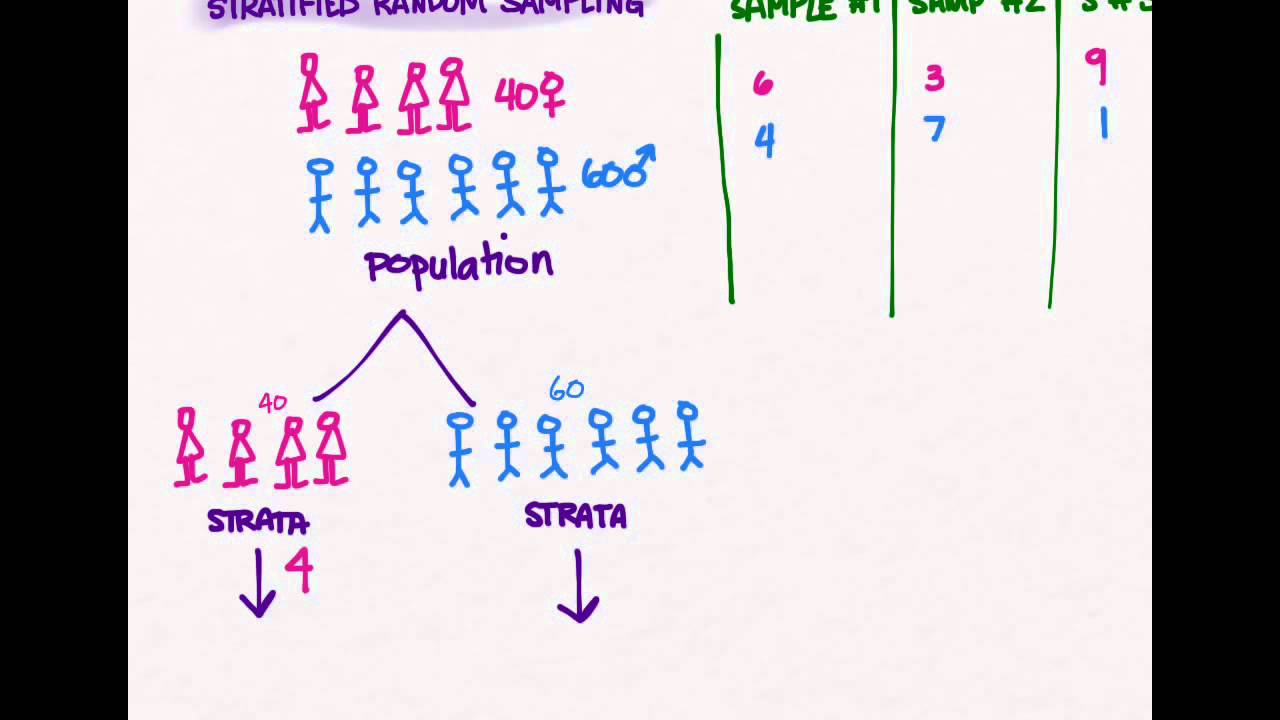
Your sampling frame should include the whole population. For instance, if your four strata contain 200, 400, 600, and 800 people, you may choose to have different sampling fractions for each stratum. Each element of the population.
tarriere toilettenbrille mit armlehnen toilette turque origine spacex merchandise india
Sampling techniquesmod5
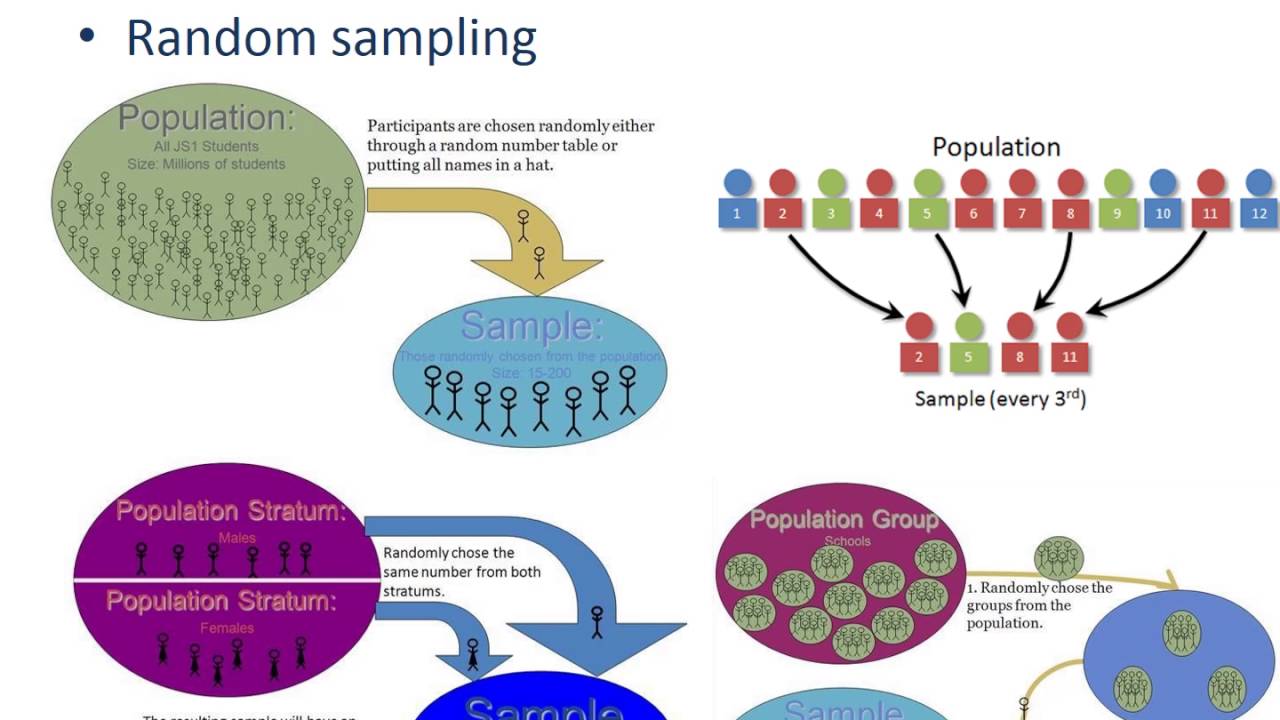
In survey methodology, systematic sampling is a statistical method involving the selection of elements from an ordered sampling frame.the most common form of systematic sampling is an equiprobability method. Cluster sampling is a method where the target population is divided into multiple clusters. This could be based on the population of a city. Random sampling is a statistical technique used in selecting people or items for research.

Your sampling frame should include the whole population. Each of the subclasses should portray comparable. Stratified sampling advantages and disadvantages. Stratified sampling refers to a random sampling technique that clubs items of the whole population into different groups based on their similar characteristics. Suppose, for example, a researcher desires to conduct a survey of all the students in a given.

When to use simple random sampling. Stratified random sampling refers to a sampling method that has the following properties. Results from probability theory and statistical theory are employed to guide the practice. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article probability sampling if you do not know what probability sampling is]. Stratified sampling is a.
Then, samples from each stratum are taken, whether proportionately or disproportionately, to conduct the research or analysis. In survey sampling, weights can be applied to the data to adjust for the sample design, particularly in stratified sampling. When to use simple random sampling. Cluster sampling and stratified sampling are probability sampling techniques with different approaches to create and analyze samples..

As opposed, in cluster sampling initially a partition of study objects is made into mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive subgroups, known as a cluster. This will only be true if the strata or groups are homogeneous. Stratified random sampling ensures that each subgroup of a given population is adequately represented within the whole sample population of a research study. Cluster.

Suppose, for example, a researcher desires to conduct a survey of all the students in a given university with 10,000 students, 8,000 females and 2,000 males. Then, samples from each stratum are taken, whether proportionately or disproportionately, to conduct the research or analysis. This sampling method is also called “random quota sampling. In business and medical research, sampling is widely.

Each element of the population. It helps ensure high internal validity: In simple random sampling each member of population is equally likely to be chosen as part of the sample. For instance, if your four strata contain 200, 400, 600, and 800 people, you may choose to have different sampling fractions for each stratum. Stratified sampling advantages and disadvantages.

When to use simple random sampling. Random sampling is a statistical technique used in selecting people or items for research. This could be based on the population of a city. It is also the most popular method for choosing a sample among population for a wide range of purposes. Results from probability theory and statistical theory are employed to guide.