28+ Hygroscopic Condensation Nuclei
Hygroscopic Condensation Nuclei. Describe the general relationship among the altitude, temperature, and composition of stratiform clouds. What is the role of hygroscopic nuclei in the process of condensation?

In the atmosphere, they promote condensation and cloud formation at values of relative humidity under 100%. There are two broad categories of condensation nuclei: A hygroscopic salt is any type of salt that can absorb moisture from.
hammerite vert jade martele hauteur lavabo pmr 2017 graham norton show logo honeywell non programmable thermostat manual
PPT Clouds, Cloud Formation, and Stability PowerPoint
All of these are correct. There are two broad categories of condensation nuclei: Nevertheless, the microphysical mechanisms of these processes remain unresolved. Condensation nuclei are formed from a variety of sources including dust, pollen, smoke, salt from ocean spray and sulfates.
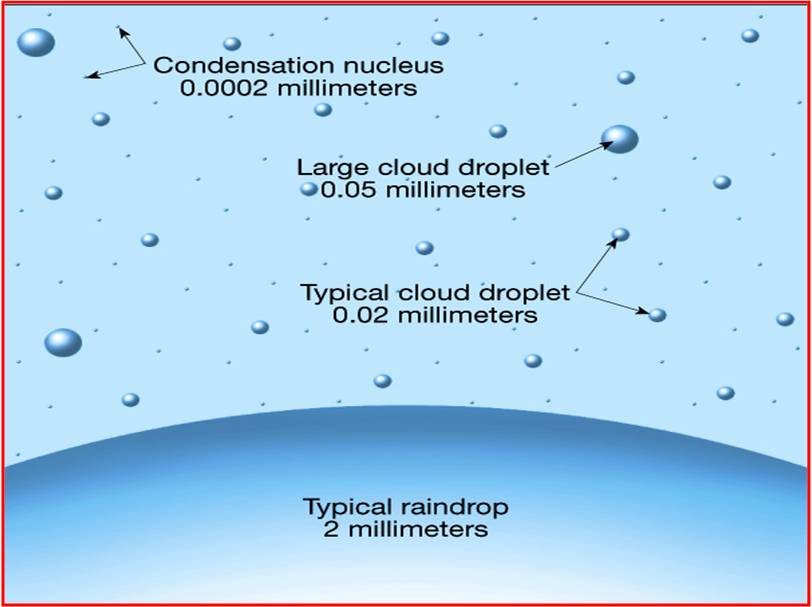
Usually, condensation occurs on a foreign surface; In the atmosphere of earth, this surface presents itself as tiny solid or liquid particles called ccns. In the atmosphere, they promote condensation and cloud formation at values of relative humidity under 100%. Hygroscopic nuclei are small particles that have a special chemical affinity (attraction) for water vapor. Water vapor condenses on hygroscopic.

Hygroscopic nuclei _____ water molecules. These nuclei resist condensation even when the relative humidity is greater than 100 percent. Condensation nucleus, tiny suspended particle, either solid or liquid, upon which water vapour condensation begins in the atmosphere. Condensation nuclei such as silver iodide allow several water crystals to combine, thereby forming large water droplets. Aerosol hygroscopicity represents the ability of.

Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription. , 15 ( 2015 ) , pp. The british naturalist who is credited with being among the first to devise a classification of cloud types is. Of sulphur dioxide, salt, dust, or smoke) in the free air, on.

In the atmosphere, they promote condensation and cloud formation at values of relative humidity under 100%. Access to the complete content on oxford reference requires a subscription or purchase. These nuclei are hygroscopic meaning they attract water molecules. Condensation nuclei such as silver iodide allow several water crystals to combine, thereby forming large water droplets. Salt nuclei can induce it.

Salt nuclei can induce it at a relative humidity of less than 80 per cent. The british naturalist who is credited with being among the first to devise a classification of cloud types is. [1] as described by the köhler theory, the hygroscopicity of atmospheric aerosol particles is a key factor regulating their cloud condensation nuclei (ccn) activity. Here we.